Article available in PDF
Human are infected chiefly by a
species of whipworm called Trichuris trichiuris or Trichocephalus
trichiuris which are round worm nematode
that causes Trichuriasis ,one of the neglected tropical disease that
infects human and animals large intestine. Because of the worm shapes (Look
like a whip with wider handles at the posterior end), It is commonly known as Whipworm.
LIFE
CYCLE
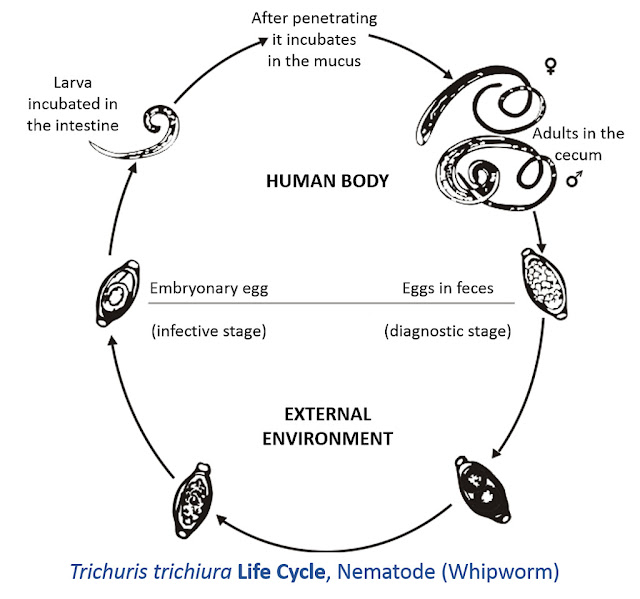
Adult worm can live up to 5 years and the female worm can lay up
to 20.000 eggs per day for an entire
lifetime. Eggs are deposited from human feces to soil where, after 2 or 3 weeks
becomes embryonated and enter the infective stage. Hence, the embryonated egg are the infective stage of T.trichiuris.
These infective eggs are ingested
and hatch in human small intestine exploiting the intestinal micro flora as
hatching stimulus. This is the location of growth, molting.Infective larvae
penetrate the Villi and continue to develop in the small intestine.The yong
worms love to the caecum and penetrate the mucosa, and there they complete
development to adult worms in the large intestine.
The life cycle from the time of
ingestion of eggs to development of mature worms takes approximately 3 months. During this time, there may be limited
signs of infection in stools samples due to lack of egg production and
shedding. The female worm begin to lay eggs after 3 months of maturity. Worms commonly live about 1 year, during
which time females can lay up to 20.000
eggs per days as earlier stated.
MORPHOLOGY
·
THE
ADULT WORM
Adult worm resembles a Whip. It has a narrow anterior
esophageal end and shorter and thicker posterior end. The worm is pinkish-white
in color and attaches to the host through their slender anterior end and feed
on tissues secretions instead of blood.
It should be noted that female worm
(35-50mm long) are larger than males ( 30-45 mm) and the females have a bluntly
round posterior end while male have coiled posterior end.
 |
| Adult worm of Trichuris trichiura |
·
THE
EGG
The eggs have a mucogelatinous plug
at each terminal end of the elongated egg that is bile-stained and barrel-shaped
(bipolar protuberances). A smooth but thick shell covers the egg that is
from 45 – 55µm in length and 20-23µm in width.
 |
| Eggs of Trichuris trichiura |
TRANSMISSION
Trichuriasis
is usually spread when people eat contaminated food or drink water that
contains eggs of the worms especially when contaminated vegetable are not fully
cleaned or cooked.
The eggs are often found in the soil
mostly in areas where people defecate outside and where untreated human feces
are used as fertilizer. Therefore the best route of transmission is fecal-oral.
Children playing in such soil and
putting their hands in their mouths can be easily infected.
Humans are the main but not the only
reservoir for Trichuris trichiura.
SIGN
AND SYMPTOMS
Minor infestations < 100 worms are
frequently asymptomatic meanwhile heavier infestation >100 worms especially
in children are symptomatic with gastrointestinal problems including abdominal
pain and distension, bloody or mucus filled diarrhea and tenesmus (feeling of incomplete defecation)
Loss of appetite, growth
retardation, weight loss, rectal prolapsed, nutritional deficiencies including
anemia (Iron deficiency and blood loss)and vitamin A deficiency which may also occur
and are characteristically sign and
symptoms of Trichuriasis.
It does not commonly cause eosinophilia like other parasitic
infections.
LABORATORY
DIAGNOSTIC
Trichuriasis
can be diagnosed when Trichuris trichiura eggs are
detected in stool examination. The egg are characterized with their elongated
shape, smooth shell and are barrel-shaped, brown unembryonated and have bipolar
plugs found in the terminal ends.
Apart from direct wet month,
concentration techniques like The Kato-katz
thick smear technique are used for identification of the eggs in stool
sample
Adult worms are rarely seen in fecal
samples but are useful in identifying an infection
PREVENTION
·
Proper sanitation especially
hand washing and waste treatment or disposal and other means of maintaining a
good sanitary environment will reduce the rate of contamination
·
Deworming
TREATMENT
- Drug commonly used are obtain by combining mebendazole or albendazole with ivermectin which is very effective even with children.
- Another drug is Diferarsone
- People with diarrhea may also be treated with Ioperamide which increases the amount of drug contact with the parasites.
Reference:
·
District Laboratory practice
in Tropical Countries (Monica CHEESBROUGH)
·
Wikipedia
·
CDC